ORTHOPANTOMOGRAM
An orthopantomogram is an X-ray image of your whole mouth, including your upper and lower jaw and teeth. The X-ray machine moves around your head while taking the image. This provides a complete ear to ear image of your mouth and teeth. It is used to: look at impacted wisdom teeth , to help find the cause of dental pain, to view the position of dental implants or to help assess teeth for orthodontic treatment.
- PREPARING FOR YOUR ORTHOPANTOMOGRAM: Before the procedure can take place, you will need to remove glasses, dentures and any jewellery from your head and neck (such as earrings and necklaces) as well as any hairclips. You must tell your doctor or radiographer if you are, or think you could be, pregnant as X-rays aren’t recommended for pregnant women unless there is an urgent medical reason.

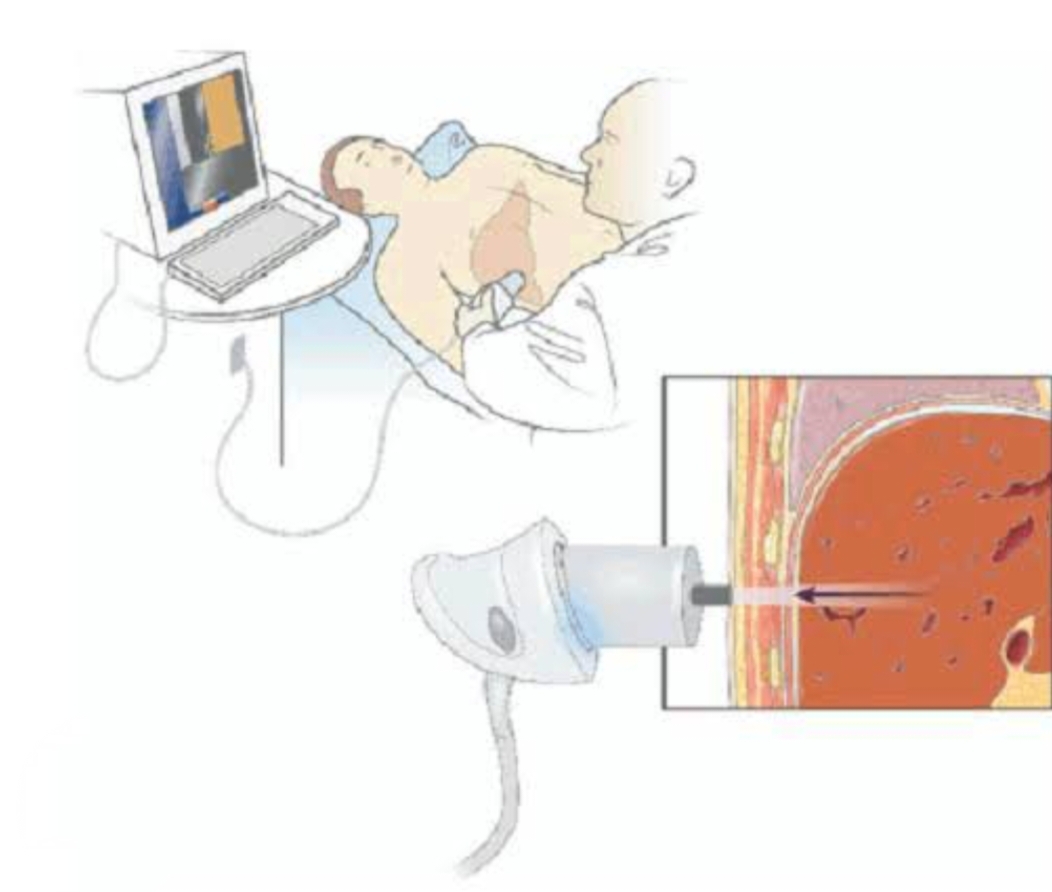
ULTRASONOGRAPHY
The steps you will take to prepare for an ultrasound will depend on the area or organ that is being examined. Your doctor may tell you to fast for eight to 12 hours before your ultrasound, especially if your abdomen is being examined. However, you can continue to drink water and take any medications as instructed. For other examinations, you may be asked to drink a lot of water and to hold your urine so that your bladder is full and better visualized.An ultrasound carries minimal risks. Unlike X-rays or CT scans, ultrasounds use no radiation. For this reason, they are the preferred method for examining a developing fetus during pregnancy.
DIGITAL X-RAYS
- HOW YOU PREPARE: Different types of X-rays require different preparations. Ask your doctor or nurse to provide you with specific instructions.
- WHAT TO WEAR: In general, you undress whatever part of your body needs examination. You may wear a gown during the exam, depending on which area is being X-rayed. You may also be asked to remove jewelry, eyeglasses and any metal objects because they can show up on an X-ray.
- CONTRAST MATERIAL: Before some types of X-rays, you’re given a liquid called contrast medium. Contrast mediums, such as barium and iodine, help outline a specific area of your body on the X-ray image. You may swallow the contrast medium or receive it as an injection or an enema.

CT SCAN
Depending on which part of your body is being scanned, you may be asked to: Take off some or all of your clothing and wear a hospital gown, to remove metal objects, such as a belt, jewelry, dentures and eyeglasses, which might interfere with image results and to refrain from eating or drinking for a few hours before your scan
- CONTRAST MATERIAL : A special dye called a contrast material is needed for some CT scans, to help highlight the areas of your body being examined. The contrast material blocks X-rays and appears white on images, which can help emphasize blood vessels, intestines or other structures.
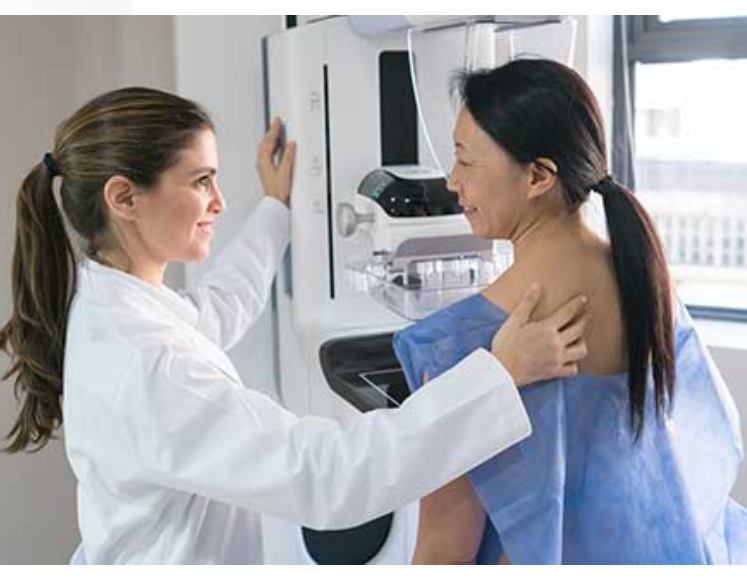
Mammography
Mammography is the process of using low-energy X-rays to examine the human breast for diagnosis and screening. The goal of mammography is the early detection of breast cancer, typically through detection of characteristic masses or microcalcifications.
A mammogram is an X-ray picture of the breast. Doctors use a mammogram to look for early signs of breast cancer. Regular mammograms are the best tests doctors have to find breast cancer early, sometimes up to three years before it can be felt. Are you worried about the cost? CDC offers free or low-cost mammograms.
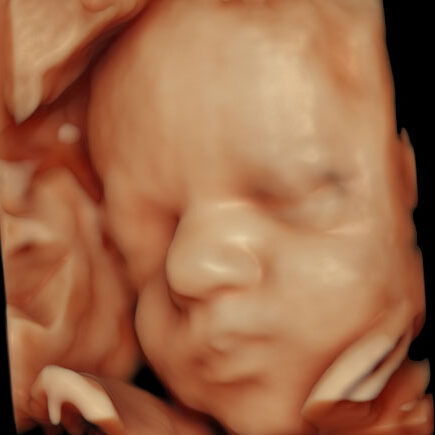
FOETAL IMAGING
- FIRST TRIMESTER SCREENING (FTS): A first trimester screening (FTS) is a combination of blood and ultrasound tests that assess the risk of a fetus having certain birth defects. It is usually performed between 11 and 14 weeks of pregnancy.
- ANOMALY SCAN WITH 4D: An anomaly scan, also known as a 20-week ultrasound or anatomy scan, is a prenatal ultrasound that checks for birth defects and other abnormalities in a fetus. It’s usually performed between 18 and 22 weeks of pregnancy.
- 4D: An anomaly 4d scan is a detailed ultrasound that uses 4D technology to examine a fetus for abnormalities. It is also known as a TIFFA scan (Targeted Imaging for Fetal anomalies) or a 20 weeks scan.
- FETAL DOPPLER SCAN: A fetal Doppler scan is a non-invasive ultrasound that uses sound waves to check the blood flow and health of a fetus. It can also detect the baby’s heartbeat and movement. This can be done from 26 weeks to term, but its’ best done between 32 and 40 weeks.
- FETAL ECHO SCAN: A fetal echo scan, also known as a fetal echo-cardiogram, is a painless ultrasound that examines an unborn baby’s heart. It shows the structure, size and function of the baby’s heart. Measures the heart’s rhythm and valves. It also shows how blood is pumped through the heart.
FIBROSCAN & ELASTOGRAPHY
Fibroscan is a type of liver elastography that uses ultrasound technology to measure liver stiffness and fat content. It is a non-invasive and painless procedure that can help doctors diagnose and monitor liver disease.